Geogrid
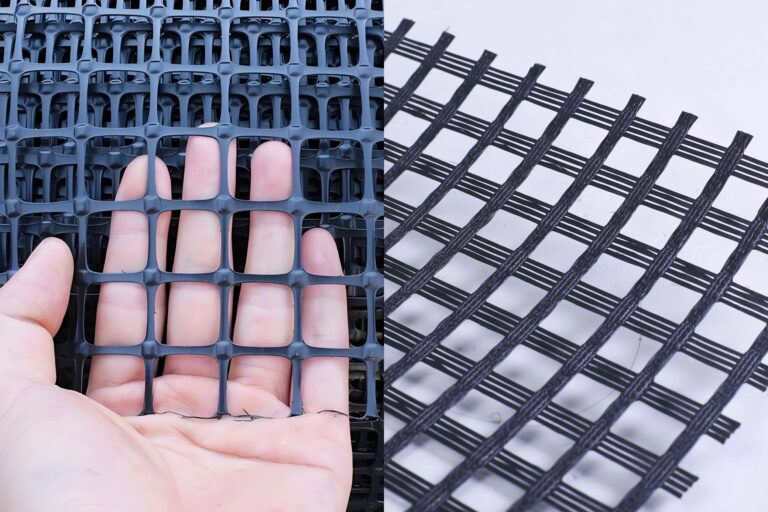
Geogrid is a geosynthetic material widely used in civil engineering. The following is a detailed introduction to geogrid:
Geogrid Description
Geogrid is made of high molecular polymer through extrusion, stretching and other processes, and has a regular grid structure. Its raw materials usually include polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), polyester (PET), etc. According to the manufacturing process and grid shape, it can be divided into unidirectional geogrid and bidirectional geogrid. The tensile strength of unidirectional geogrid is higher in one direction, while bidirectional geogrid has good tensile strength in both vertical and horizontal directions.
Geogrid Features
-High tensile strength
Geogrid has high tensile strength and can withstand large tensile loads without breaking. For example, in road engineering, it can effectively disperse the stress generated by vehicle loads and avoid cracks and deformation of the road surface.
-Strong anti-deformation ability
Even under large external forces, geogrids can maintain good shape and structural stability. This allows it to effectively play its reinforcement and stabilization role when subjected to long-term loads or dynamic loads.
-Good corrosion resistance
Because it is mainly made of high molecular polymers, it has good chemical corrosion resistance and can be used for a long time in harsh environmental conditions, such as in soil environments with chemical erosion or humid environments.
-Good interaction with soil particles
The grid structure on the surface of the geogrid can be tightly combined with soil particles to form an integral composite structure. This composite structure can increase the friction and bite force of the soil, and improve the shear strength and stability of the soil.
Scope of application of geogrids
-Road engineering
Laying geogrids in the base and subbase of roads can enhance the bearing capacity of roads, reduce rutting and cracks on the road surface, and extend the service life of roads. Especially when building roads on soft soil foundations, geogrids can effectively improve the stability of the foundation.
-Railway Engineering
Used for the reinforcement and stabilization of railway roadbeds, preventing the settlement and deformation of the roadbed, and ensuring the safety and comfort of train travel.
-Slope Protection Engineering
Laying geogrids on the slopes can enhance the anti-slip ability of the slope soil and prevent slope collapse and landslides. At the same time, it can also be combined with vegetation to form ecological slope protection and play a role in beautifying the environment.
-Water Conservancy Engineering
In water conservancy projects such as dams and river banks, geogrids can be used to reinforce soil, prevent water scouring and erosion, and improve the stability and safety of water conservancy projects.
